By the Numbers: 3 January 2022
9.6 Million
The number of "beneficiaries" served by Military Health System (MHS) in the U.S. and abroad, according to a recently updated Congressional Research Service report -- Military Medical Care: Frequently Asked Questions.
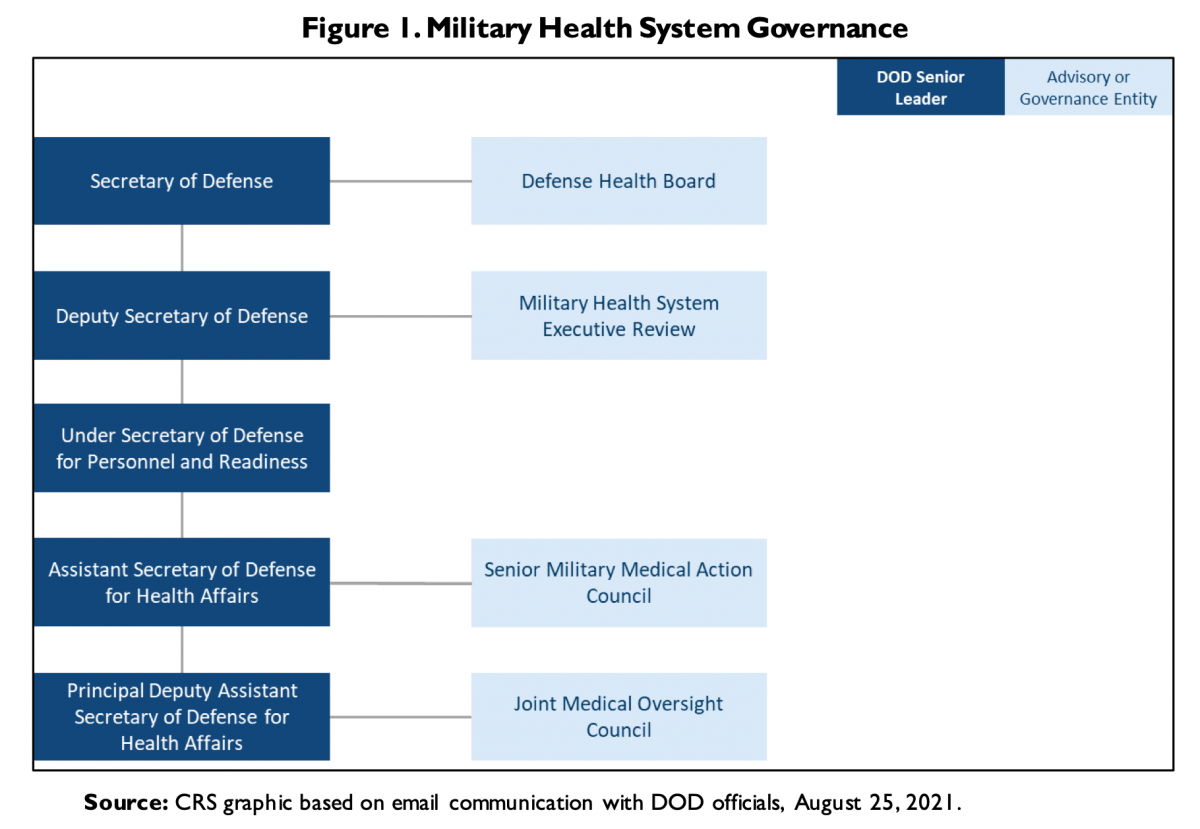
Military medical care is a congressionally authorized entitlement that has expanded in Analyst in Defense Health size and scope since the late 19th century. Chapters 55 and 56 of Title 10, U.S. Code Care Policy entitle certain health benefits to military personnel, retirees, and their families. These health benefits are administered by a Military Health System (MHS). The primary objectives of the MHS, which includes the Defense Department’s hospitals, clinics, and medical personnel, are (1) to maintain the health of military personnel so they can carry out their military missions, and (2) to be prepared to deliver health care during wartime. Health care services are delivered through either Department of Defense (DOD) medical facilities, known as military treatment facilities (MTFs), as space is available, or through networks of participating civilian health care providers. As of 2020, the MHS operates 721 MTFs, employs nearly 61,000 civilians and 78,000 military personnel, and serves 9.6 million beneficiaries across the United States and in overseas locations.
9.6 Million
The number of "beneficiaries" served by Military Health System (MHS) in the U.S. and abroad, according to a recently updated Congressional Research Service report -- Military Medical Care: Frequently Asked Questions.
Military medical care is a congressionally authorized entitlement that has expanded in Analyst in Defense Health size and scope since the late 19th century. Chapters 55 and 56 of Title 10, U.S. Code Care Policy entitle certain health benefits to military personnel, retirees, and their families. These health benefits are administered by a Military Health System (MHS). The primary objectives of the MHS, which includes the Defense Department’s hospitals, clinics, and medical personnel, are (1) to maintain the health of military personnel so they can carry out their military missions, and (2) to be prepared to deliver health care during wartime. Health care services are delivered through either Department of Defense (DOD) medical facilities, known as military treatment facilities (MTFs), as space is available, or through networks of participating civilian health care providers. As of 2020, the MHS operates 721 MTFs, employs nearly 61,000 civilians and 78,000 military personnel, and serves 9.6 million beneficiaries across the United States and in overseas locations.